Authentication details¶
If you are using one of our SDKs or templates, you can probably skip this page. This page is useful primarily as a reference for interacting with the platform using raw HTTP requests or clients written in languages where we don't provide SDK.
Support OpenID Connect¶
OpenID Connect is built on the OAuth 2.0 protocol and uses an additional JSON Web Token (JWT), called an ID token, to standardize areas that OAuth 2.0 leaves up to choice, such as scopes and endpoint discovery. It is specifically focused on user authentication and is widely used to enable user logins on consumer websites and mobile apps.
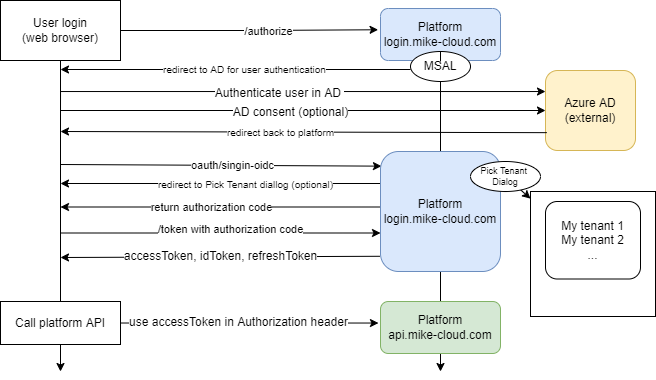
User credentials flow with PKCE¶
- Platform's OAuth service delegates the authentication part of the flow to External Azure AD
- To authenticate, user must be registered as valid user in External AD. User can be invited by existing user or Customer service.
- Using user credentials with OAuth2 authentication flow requires that an application is registered in the platform.
Flow diagram:
Access token¶
The resulting access token sample
{
"oid": "<user id>",
"aud": [
"platform",
"<app id>"
],
"sub": "<user name>",
"TenantId": "<tenant id>",
"client_id": "<app id>",
"scope": "openid offline_access",
"jti": "780f4749-386d-40e8-ade3-497f212f92da",
"exp": 1670253182,
"iss": "https://login.mike-cloud.com/",
"iat": 1670249582
}
Client libraries¶
Any OpenID Connect enabled library can be used to connect to the platform
dotnet client libraries for desktop applications¶
We recommend using IdentityModel.OidcClient nuget package. Sample configuration for production environment
var options = new OidcClientOptions()
{
Authority = "https://login.mike-cloud.com",
ClientId = <registered app id>,
Scope = "openid offline_access",
RedirectUri = <value from registraiton>,
Browser = <depnds on UI stack>,
LoadProfile=false
};
var oidcClient = new OidcClient(options);
var result = await _oidcClient.LoginAsync();
AccessToken: use in platform API calls , see belowRefreshToken: use for silent refresh of access token by callingoidcClient.RefreshTokenAsync(refreshToken);User.Claims: extracted information from the tokens
Sample result usage:
if (!result.IsError)
{
var token = result.AccessToken;
var claims = result.User.Claims;
var user = new {
DisplayName = claims.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Type == "sub")?.Value,
UserId = claims.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Type == "oid")?.Value,
Email = claims.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Type == "email")?.Value,
CustomerGuid = claims.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Type == "TenantId")?.Value,
CustomerName = claims.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Type == "TenantName")?.Value,
Roles = claims.Where(x => x.Type == ClaimTypes.Role).Select(v=>v.Value).ToArray(),
};
}
Backend service token validation in dotnet application¶
In dotnet applications that want to authorize directly to the platform's OAuth server, validate the issuer and audiences when setting up the authentication:
var IssuerUrl = "https://login.mike-cloud.com"; // for production
// var IssuerUrl = $"https://login.mike-cloud-{environment.ToString().ToLower()}.com"; // for non production
var allowAudiences = new List<string> { "<Client ID>"};
// ...
services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
options.Authority = IssuerUrl;
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidAudiences = allowAudiences
};
});
Javascript, Python Client libraries¶
There are multiple OpenID client libraries, for detailed example of React SPA sample usage see here.
Access token usage¶
- User retrieves access token for the platform services as part of the login flow and adds it in the request headers (as standard Authorization header / Bearer token);
- Platform services will validate the token and allow the request to proceed.
"api-version": "3",
"Authorization": "Bearer {}".format(token),
"dhi-service-id": "<guid>",
"dhi-project-id": "<guid>",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
Click to show example shell script to start an engine execution using user credentials
projectId="<replacewithprojectid>" userId="<replacewithuserid>" customerId="<replacewithcustomerid>" token="<replacewithbearertoken>" # create execution curl -L -X POST "https://api.mike-cloud-test.com/api/compute/execution" \ -H 'api-version: 2' \ -H 'dhi-service-id: engine' \ -H "dhi-project-id: $projectId" \ -H "dhi-user-id: $userId" \ -H "dhi-customer-guid: $customerId" \ -H "Authorization: $token" \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --data-raw '{ "inputs": [ { "uri": "https://coreenginedev0inputs.blob.core.windows.net/data/lake.m21fm", "engine": "FemEngineHD" }, { "uri": "https://coreenginedev0inputs.blob.core.windows.net/data/lake.mesh" } ], "options": { "poolType": "VM-S-5", "nodeCount": 1 } }'
Using Open API Account¶
Project owners can create Open API account and generate an Open API key in Cloud Admin application. The account can then be added to a project in Cloud Admin and key used for requests to MIKE Cloud Platform. You can learn more about it here. After that, clients can send requests with the following headers:
"api-version": "1",
"dhi-open-api-key": "<guid>",
"dhi-service-id": "<guid>",
"dhi-project-id": "<guid>",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
Never expose Api Key in open client communication , like browser. The API Key is like password and is intended to be used only in secured environments.
Click to show example shell script to start an engine execution using Open API key
projectId="<replacewithprojectid>" openapikey="<replacewithopenapikey>" # create execution curl -L -X POST "https://api.mike-cloud-test.com/api/compute/execution" \ -H 'api-version: 2' \ -H 'dhi-service-id: engine' \ -H "dhi-project-id: $projectId" \ -H "dhi-open-api-key: $openapikey" \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --data-raw '{ "inputs": [ { "uri": "https://coreenginedev0inputs.blob.core.windows.net/data/lake.m21fm", "engine": "FemEngineHD" }, { "uri": "https://coreenginedev0inputs.blob.core.windows.net/data/lake.mesh" } ], "options": { "poolType": "VM-S-5", "nodeCount": 1 } }'
Request headers¶
Depending on the authentication mode as well as the service in question, there can be required and/or different optional headers available. The full list of available headers is provided below. In general, you need to be aware of these headers only if you are interacting with the Platform using raw HTTP requests. If you are using our dotnet or Python SDK, you don't need to worry about them.
| Header name | Header value | Description |
|---|---|---|
dhi-project-id |
guid |
Identifies the project context for the request. If the project id or dataset id is already part of the url path, then it may not be necessary to send this header, otherwise it may be needed to indicate the correct context of the request. |
dhi-dataset-id |
guid |
Identifies the dataset for the request. If the dataset id is already part of the url, then it may not be necessary to send this header. |
dhi-service-id |
guid |
Is required when calling service via Metadata service, not required since api-version 3 |
dhi-recursive-token |
bool |
Is required in some services to indicate that the context of the request should include also subfolders |
dhi-open-api-key |
guid |
Is required when using Open API Account for authentication |
dhi-sas-token |
string |
Is used when calling service directly |
Authorization |
string |
Is required when using user credentials for authentication |
api-version |
string |
|
Content-Type |
string |
|
Accept-Encoding |
string |
You can retrieve the list of service ids using the following end point:
GET/api/services/ids